Aggregate Models
Aggregate Models(All parts of the economy taken as a whole)
Aggregate Demand (AD): Curve that shows the amount consumers are willing / able to buy at given price level.
 Slopes down
Slopes down- Wealth Effect: as prices increase, income purchasing power falls
- Foreign Purchases Effect: as prices rise, US goods are more expensive and therefore demanded less by foreign consumers.
 Consumption (C) of Goods and Services by the Private Sector
Consumption (C) of Goods and Services by the Private Sector - Future Expectations: How will the public react to fears of the future?
- Indebtedness: Will, or can, the public keep borrowing into the future?
- Net Income: How much money is left after paying taxes?
 Gross Investment (Ig) Businesses must first use resources before selling.
Gross Investment (Ig) Businesses must first use resources before selling.- What effect will interest rates have on business’ ability to borrow?
- What kind of expectations will business have for future profits?
- What kind of profits will exist after taxes and dividends are paid?
- How quickly can new technology be applied to better construction?
- Is there already excess capacity available for short term growth?

 Government (G)
Government (G)- How much will government spend on goods and services?
- Net income being sent back to the US versus Remittances from the US
- Value changes in the US Dollar and the effect on export/import prices
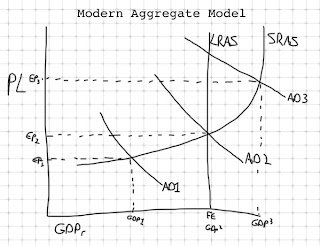
Aggregate Supply (AS): curve showing the relationship between the price level and the amount of real domestic output firms produce
Slopes up: as PL increases, GDPr increases.
 Shifters
Shifters The cost and availability of resources
- The cost of paying for resources to build stuff
- How much Land, Labor, Capital, Entrep., Foreign Resources, Tech.?
- How much of the market (and pricing/profits) can this company control?
- How efficient and productive is the labor force and the technology applied?
- What are the tax burdens on producers?
- What subsidies are available?
- What are the costs of dealing with governmental regulations?
Long Run Aggregate supply (LRAS): Measure of supply in the long run, with all resources variable.
- no relationship between PL and Q of output in the long run.
Vertical line: economy operating at efficiency.
Shifters:
(When LRAS shifts, so does SRAS)
Cover:
- Inflationary gap
- Recessionary gap
- Equilibrium